|
Nana C++ Library. Reference for users.
What we need to use nana
|
|
Nana C++ Library. Reference for users.
What we need to use nana
|
Layout management - an object of class place is attached to a widget, and it automatically positions and resizes the children widgets. More...
Classes | |
| class | error |
| struct | implement |
Public Types | |
| using | field_reference = field_interface & |
| reference to a field manipulator which refers to a field object created by place More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| place () | |
| place (window) | |
| Attaches to a specified widget. More... | |
| ~place () | |
| void | bind (window handle) |
| Bind to a window. More... | |
| window | window_handle () const |
| void | splitter_renderer (std::function< void(window, paint::graphics &, mouse_action)> fn) |
| void | div (std::string div_text) |
| Divides the attached widget into fields. May throw placa::error. More... | |
| const std::string & | div () const noexcept |
| Returns div-text that depends on fields status. More... | |
| void | modify (const char *field_name, const char *div_text) |
| Modifies a specified field. May throw placa::error. More... | |
| field_reference | field (const char *name) |
| Returns a field with the specified name. More... | |
| void | field_visible (const char *field_name, bool visible) |
| <Shows/Hides an existing field. More... | |
| bool | field_visible (const char *field_name) const |
| Determines whether the specified field is visible. More... | |
| void | field_display (const char *field_name, bool display) |
| Displays/Discards an existing field. More... | |
| bool | field_display (const char *field_name) const |
| Determines whether the specified field is displayed. More... | |
| void | collocate () |
| Layouts the widgets. More... | |
| void | erase (window handle) |
| Erases a window from field. More... | |
| field_reference | operator[] (const char *name) |
| Returns a field with the specified name. Equal to field();. More... | |
| template<typename Panel , typename... Args> | |
| place & | dock (const std::string &dockname, const std::string &factory_name, Args &&...args) |
| Add a panel factory. More... | |
| place & | dock (const std::string &dockname, std::string factory_name, std::function< std::unique_ptr< widget >(window)> factory) |
| widget * | dock_create (const std::string &factory) |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static bool | valid_field_name (const char *name) |
Layout management - an object of class place is attached to a widget, and it automatically positions and resizes the children widgets.
Generally, an object of class place attachs to a widget, and it automatically positions and resizes widgets which are the children of the attached widget.
see http://www.nanapro.org/en-us/help/utilities/place.htm
The class place is used for layout management. Generally, an object of class place binds to a widget, and automatically positions and resizes the widgets which are the children of the that widget. The desired format or layout is set with div(const char* div_text); which cause a default or root field (surface of the attached widget), to be divided into others fields in the specified manner using the position rules described below. Then the children widgets are inserted into the desired field for layouting using a map-like notation. If the field name specified is not (or will not) present in the div-text, an invisible field is creates and all widgets corresponding to the field will be hidden. An entire field can be temporary retired from the view using field_display(const char* name, bool display);. A widget can be retired from a field using erase(window handle);. A field can be also set invisible with field_visible(const char* name, bool visibility);. The difference is that an invisible field still occupy the space, while a field not displayed - not. Finally collocate(); collocates the fields and widgets through the rule set in div(). In most cases, place collocates automatically when the binded window resizes. But when you reset a new divide text collocate() should be invoked manually, otherwise the widgets will not be positioned until the place binded window is resized.
In develop: void modify (const char *field_name, const char *div_text) method to modifie a specified field.
template<typename Panel , typename... Args> void dock (const char *dockname, Args &&...args) - Add a panel factory
The field is a basic concept for place. There are four different types of fields. Each type describes how widgets are positioned. These types of fields are:
| Field type | Description |
|---|---|
| Horizontal | Widgets are positioned horizontally, such as the buttons in a Windows task bar. This is the default. |
| Vertical | Widgets are positioned vertically, such as the items in a menu. |
| Grid | Widgets are positioned like a grid, such as keys on the keyboard. |
| Splitter | A splitter bar is used for adjusting the size of fields on both sides of it. |
< and >, |, %, [ and ], arrange, collapse, gap, grid, margin min or max, repeated, variable, vertical or vert, weight,
The divide-text is used to divide a widget into fields to position and resize its children widgets.
<>
<<>>
There is an implicit root field. All the fields defined by divide-text are children of root field.
<a>|<b> or <a>|30<b> or <a>|30%<b> ; <horizontal <a>|<b>> ; <vertical <a>|<b>>
Sets a splitter bar between field a and b. It can be vertical or horizontal. When a number is specified behind |, it stands for an initial weight of the right field. 30% indicates the percent of total pixels = (weight of a + weight of b)*30%. In such cases the attribute weight will be ignored if specified for a or b.
[1,2,3]
An array that has the elements 1, 2 and 3 - three elements.
[1,2,3,repeated]
The keyword repeated indicates the array is countless, and its elements are 1,2,3,1,2,3,1,2,3...
[1,2,variable,3]
The keyword variable is an unspecified value. It is interpreted differently by different attributes of field(arrange, gap, margin). Refer to Attributes of field section for more details.
Specify an identifier for a name of field
< __id_you_specified__ >
The field is named id_you_specified, and we can refer to it by using:
place_obj.field("id_you_specified")
or
place_obj["id_you_specified"]
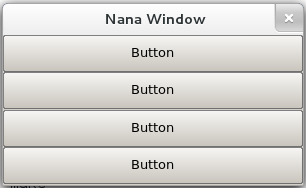
Specify a field wich all its children fields laied out vertical. If it is not specified, its children fields are laied out horizontally defaultly. For example:

If we replace this line:
plc.div("<abc>");
into
plc.div("<vertical abc>");
we will get
It stands for the width or height of a field. It depends on the type of its owner field's layout.
Specify the weight in pixel:
<abc><weight=200 def>
If the width of the form is 1000px, the field abc is 800px and def is 200.
<abc><weight=60% def><ghi>
If the width of form is 1000px, the field abc is 200px, def is 600px and ghi is 200px.
Specifies the minimized or maximized weight for a field. If a field is specified with weight and min/max at same time, the weight attribute will be ignored.
Specifies weights for a group of widgets.
place.div("<abc arrange=[50,100]>");
place.field("abc")<<btn0<<btn1;
If the number of widgets in the field is larger than the number of elements in arrange, the extra widgets will be resized by place.
place.div("<abc arrange=[50,100]>");
place.field("abc")<<btn0<<btn1<<btn2<<btn3;
Specifie variable in the array to indicates a corresponding widget's weight is not specified, and the widget will be resized by place.
place.div("<abc arrange=[30,variable,60,repeated]>");
place.field("abc")<<btn0<<btn1<<btn2<<btn3<<btn4<<btn5<<btn3;
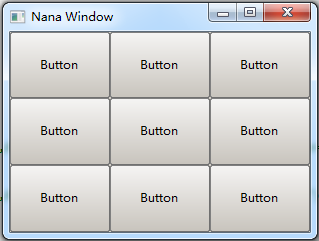
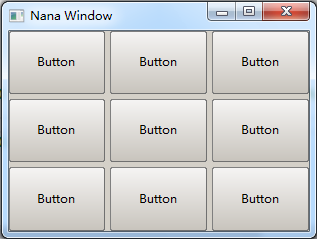
It specifies a field that lays its children widgets out as a grid. For example into a 3x2 block
<grid [3, 2]>
The field is divided a 3 X 2 grid. For 3x3:
place plc(fm);
plc.div("< abc grid=[3,3]> ");
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<button>> btns;
for(auto i = 0; i < 9; ++i) {
btns.emplace_back(new button(fm));
btns.back()->caption(L"Button");
plc.field("abc")<<btns.back()->handle();
}
Merges blocks.
<grid=[3,2] collapse(0,1,3,1)>
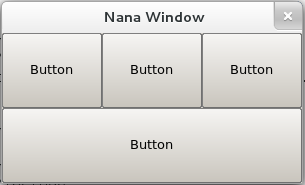
It can be specified with more than one collapse, but overlapped collapses will be ignored.
<grid=[3,2] collapse(0,1,3,1) collapse(1,1,2,2)>
The second collapse is ignored, because of overlap with the first.
It specifies a gap in pixel between widgets in any field.
<grid [3, 2] gap=5>
When a field is a grid, gap can be specified by an Array, but it always uses the first element, other elements will be ignored. the first element of array is variable for gap, the variable here is interpreted as zero.
<grid=[3,3] gap=[variable]>
is equal to
<grid=[3,3] gap=0>
The gap can also work with arrange.
<arrange=80 gap=5>
gap=5 is equal to gap=[5,repeated]
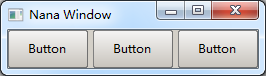
Gaps only appear between widgets. gap interprets an array differently than other attributes. Refer to margin and arrange for more details.
Specifies the empty space at sides of the place field. It can have from 1 to 4 values
<margin=[10,20,30,40]>
top margin = 10
right margin = 20
bottom margin = 30
left margin = 40
<margin=[10,20,30]>
top margin = 10
right margin = 20
bottom margin = 30
<margin=[10,20]>
top and bottom margin = 10
left and right margin = 20
<margin=[10]>
top margin = 10
<margin=20>
top, right, bottom and left margin = 10
If variable is specified in the array, it stands for zero.
<margin=[variable]>
top margin = 0
<margin=[variable,repeated]>
top, right, bottom and left margin = 0
Let's create a user interface for login validation. The program GUI looks like:
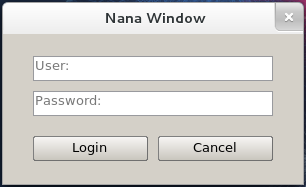
First of all, we should divide the form into fields. For this result, it may be divided like this
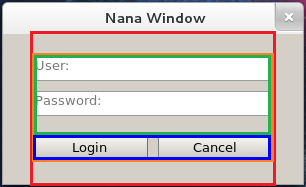
The divide-text of red rectangle should be:
<><weight=80% vertical children_fields_of_red_rectangle><>
The root field is horizontal defaultly, so these 3 fields are laied out horizontally. The red rectangle in the middle takes 80% spaces, we specify its weight is 80%. As you see, the children of red rectangle are laied out vertically, it should be specified by vertical.
The divide-text of orange rectangle:
<><weight=70% vertical children_fields_of_orange_rectangle><>
The orange rectangle is laied out in the middle about 70% space, it also specified with vertical. The divide-text of green and blue rectangles:
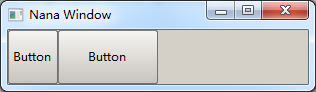
<vertical gap=10 textboxs arrange=[25,25]> <weight=25 gap=10 buttons>
The widgets in green rectangle are laied out vertically, and widgets in blue rectangle are laied out horizontally, so we only specify the vertical for the green rectangle. The usr and pswd are single-line textboxs, and we should specify them with a fixed height. And the blue rectangle manages buttons and it is horizontal, in other words, the height of blue rectangle is same as buttons', so we specify its weight is 25 pixels. We will refer to these 2 fields to insert widgets into them, so a name is given for each field.
The combination of these divide-texts:
<><weight=80% vertical <><weight=70% vertical <vertical gap=10 textboxs arrange=[25,25]> <weight=25 gap=10 buttons>><>><>
Let's start programming: (place_login.cpp)

| using nana::place::field_reference = field_interface & |
reference to a field manipulator which refers to a field object created by place
| nana::place::place | ( | ) |
| nana::place::place | ( | window | wd | ) |
Attaches to a specified widget.
| nana::place::~place | ( | ) |
| void nana::place::bind | ( | window | handle | ) |
Bind to a window.
| handle | A handle to a window which the place wants to attach. |
| void nana::place::collocate | ( | ) |
Layouts the widgets.
| void nana::place::div | ( | std::string | div_text | ) |
Divides the attached widget into fields. May throw placa::error.
|
noexcept |
Returns div-text that depends on fields status.
|
inline |
Add a panel factory.
| place & nana::place::dock | ( | const std::string & | dockname, |
| std::string | factory_name, | ||
| std::function< std::unique_ptr< widget >(window)> | factory | ||
| ) |
| widget * nana::place::dock_create | ( | const std::string & | factory | ) |
| void nana::place::erase | ( | window | handle | ) |
Erases a window from field.
| place::field_reference nana::place::field | ( | const char * | name | ) |
Returns a field with the specified name.
| void nana::place::field_display | ( | const char * | field_name, |
| bool | display | ||
| ) |
Displays/Discards an existing field.
| bool nana::place::field_display | ( | const char * | field_name | ) | const |
Determines whether the specified field is displayed.
| void nana::place::field_visible | ( | const char * | field_name, |
| bool | visible | ||
| ) |
<Shows/Hides an existing field.
| bool nana::place::field_visible | ( | const char * | field_name | ) | const |
Determines whether the specified field is visible.
| void nana::place::modify | ( | const char * | field_name, |
| const char * | div_text | ||
| ) |
Modifies a specified field. May throw placa::error.
| place::field_reference nana::place::operator[] | ( | const char * | name | ) |
Returns a field with the specified name. Equal to field();.
| void nana::place::splitter_renderer | ( | std::function< void(window, paint::graphics &, mouse_action)> | fn | ) |
|
inlinestatic |
| name | must begin with _a-zA-Z |
| window nana::place::window_handle | ( | ) | const |